fungi life cycle pdf
Evolution Characteristics and Life Cycle Author. Diversity of Fungi Page 4 of 16 u Phylum Plasmodiophoromycota Q Obligate intracellular parasites of plants algae or fungi Q Best example.

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Dikaryotization is an essential feature in the life-cycle of rusts smuts and some allied fungi Petersen 1974 Littlefield Heath 1979 Coelho et al.

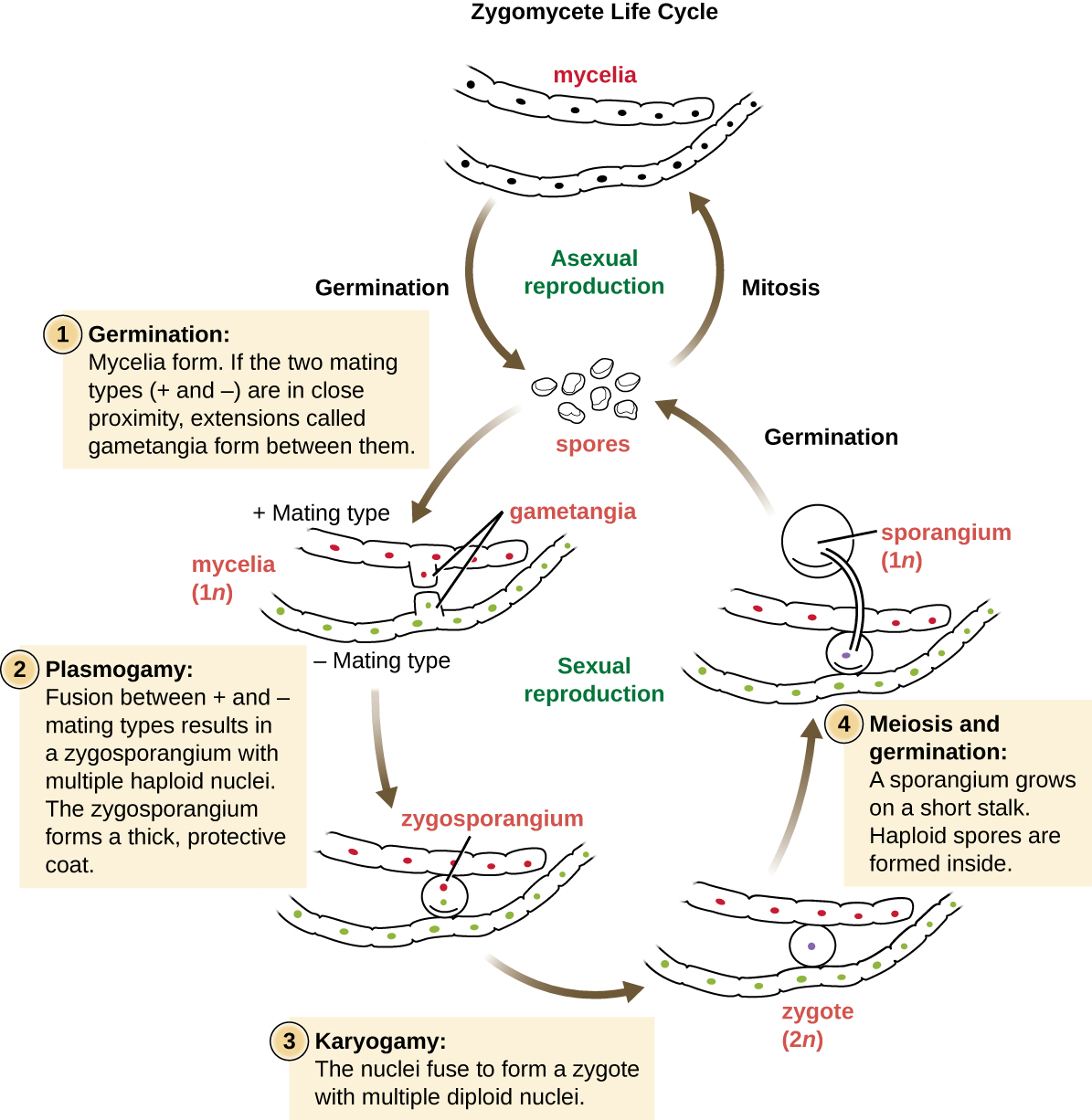
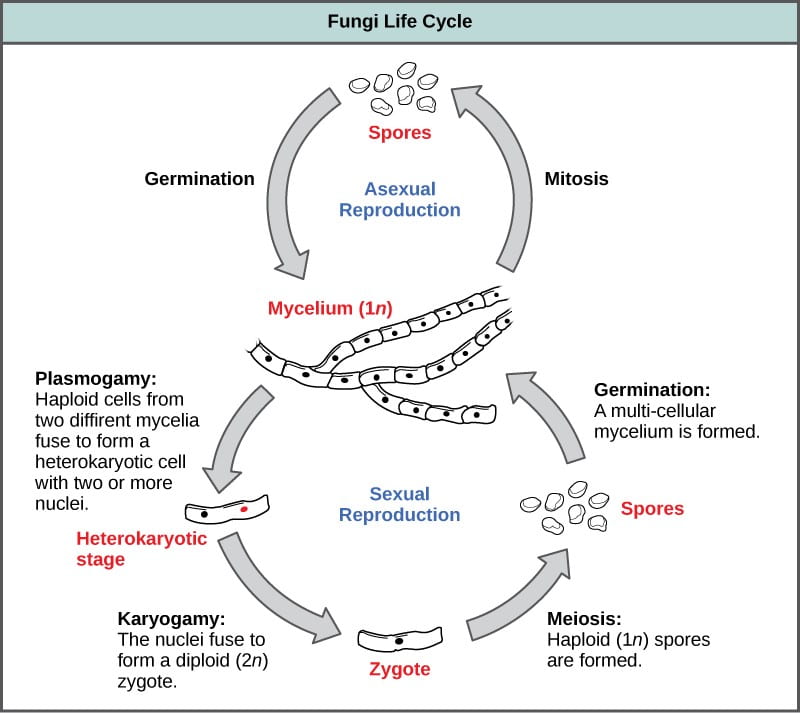
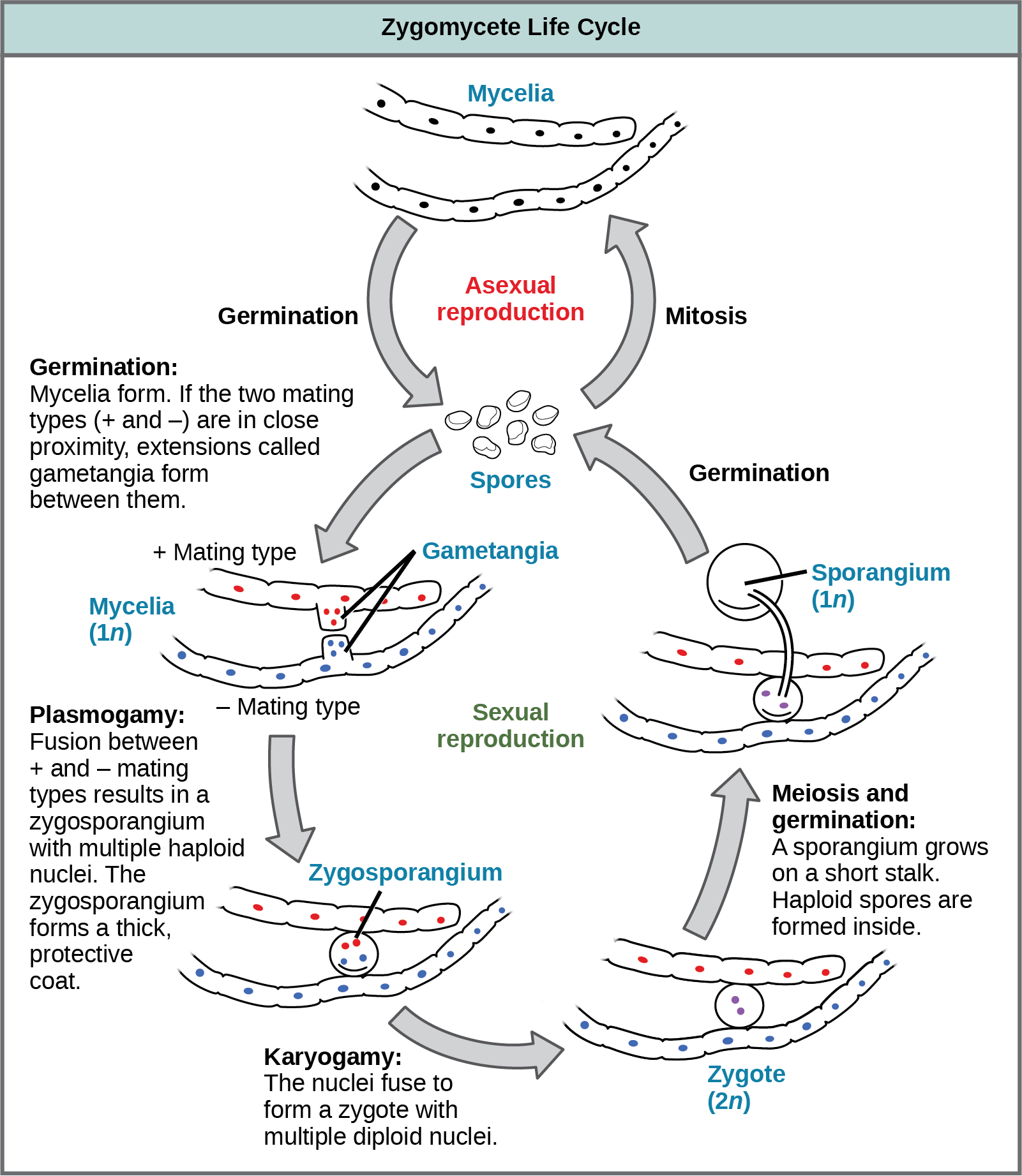
. Most of the lower fungi plasmogamy is immediately followed by karyogamy and meiosis. Monokaryotic mycelium uninucleate Mycelium contains single nucleus that usually forms part of haplophase in the life cycle of fungi. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi.
Bernice Speer Last modified by. Filamentous fungi possess a yeast-like phase at some point in their life cycle. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
How fungi establish themselves and how you can help make this happen in your garden. This phase of fungal life cycle is called dikaryophase. And life cycles of major taxa of fungi.
Chapter 31 Fungi Multiple-Choice Questions 1 Which of the following do all fungi have in common. This tutorial illustrates the relationships among these phases in the life cycle of a mushroom. In higher fungi karyogamy is often delayed so that the hyphae remain dikaryotic.
Such fungi complete their life cycle in three phases a haplophase a dikaryophase and a diplophase. How fungi are different from plants and actually are a lot more like animals this includes you. Some reproduce only sexually others only asexually.
Therefore we are going to look at the life cycle of a fungi in asexual and sexual stage. If you continue to browse the site you receive the use of cookies. All about spores and how they work in your garden ecosystem to help.
There are accessory means of multiplication of this phase in the life cycle. It consists of the ascospores parent mycelium antheridia when present and young ascogonia. Download full-text PDF Read full-text.
618 A represents the vegetative or somatic phase of the fungus. With the host protoplasm. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi.
The Rust Fungi James A Kolmer USDA-ARS St. On-screen Show Other titles. Sexual Reproduction of Fungi Spore Haploid.
In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of pythium with the help of suitable diagrams. Life cycle of fungi. Brassicae by undergoing rapid cell expansion and division forming galls that require.
Plasmodiophora brassicae l Infection of plant roots leads to club foot l Plant responds to infection by P. Life Cycle of Fungi. It is well developed and coenocytic.
While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. Manybut not allfungi reproduce both A Figure 315 sexually and asexually. Bernice Speer Created Date.
9272008 83607 PM Document presentation format. All fungi begin their life cycle in. Reproduction is by budding of yeast cells.
All students will be required to present a report on a selected topic of interest as part of the course requirements. Life Cycle of Fungi. In the life cycle it starts with the formation of ascospores and ends with the formation of dikaryons in the ascogonium.
Intercellular hyphae of many fungi especially of obligate parasites of plants fungi causing downy mildews powdery mildews and rusts obtain nutrients through haustoria. It is done by the formation of conidia. The dikaryotic phase in which cells in a fun-gal mycelium have two nuclei.
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cellsMeiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates. KnowledgeComprehension 2 The hydrolytic digestion of which of the following should. A phase of life that is unique to fungi.
Somatic Phase in Pythium. It presents a white fluffy appearance and consists of long rather slender. Learning Objectives Know the structures involved in.
The life cycle of rusts can be complex. Paul Minnesota USA Maria E Ordonez Quito Ecuador James V Groth Coleville Washington USA The rust fungi are a monophyletic group of approximately 7000 species in the basidiomycota and are highly specialized obligate parasites of plants. Classification of fungi morphology and structure Pathogenicity Diagnosis Useful Properties of Fungi Diverse group of chemo heterotrophs Over 100000 fungal species identified Only about 100 are human or animal pathogens Saprophytes Digest dead organic matter.
A meiosis in basidia B coenocytic hyphae C sexual life cycle D absorption of nutrients E symbioses with algae Answer. The basidiospores are ejected and. Fungi life cycle ppt SlideShare uses cookies to optimize website functionality and performance as well as presents more relevant advertising to our users.
The whole life cycle of wood-loving macro-fungi from mushroom back around to mushroom. Lived haploid mycelia O When mature. While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually.
Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. Cycles in fungi beginning with relatively simple life cycles Please realize that each of the major groups of fungi has a diversity of life cycles beyond those listed here. Each spore will grow into a new hypha and mycelium if it lands on a suitable substrate.
Generalized life cycle Of fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium.
Life cycle of Rhizopus Asexual reproduction Sporangiophores grow up from the substrate Cells within the sporangium divide by mitosis to produce spores haploid The sporangium dries out in the right conditions and opens releasing many spores. Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. Candida albicans ascomycete is an asexual animal pathogen.
The basidiospores germinate and grow into short. A dikaryotic filament developed from. Also focus on major fungal infections their etiologies three lecture exams and three lab exams will be given during the course.
Biology of Fungi Lecture 2.

Life Cycle Of A Macrocyclic Heteroecious Rust A Mature Diploid Download Scientific Diagram

Basidiomycota An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Reproduction In Fungi Asexual And Sexual Methods Online Biology Notes

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com

Aquatic Fungi An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
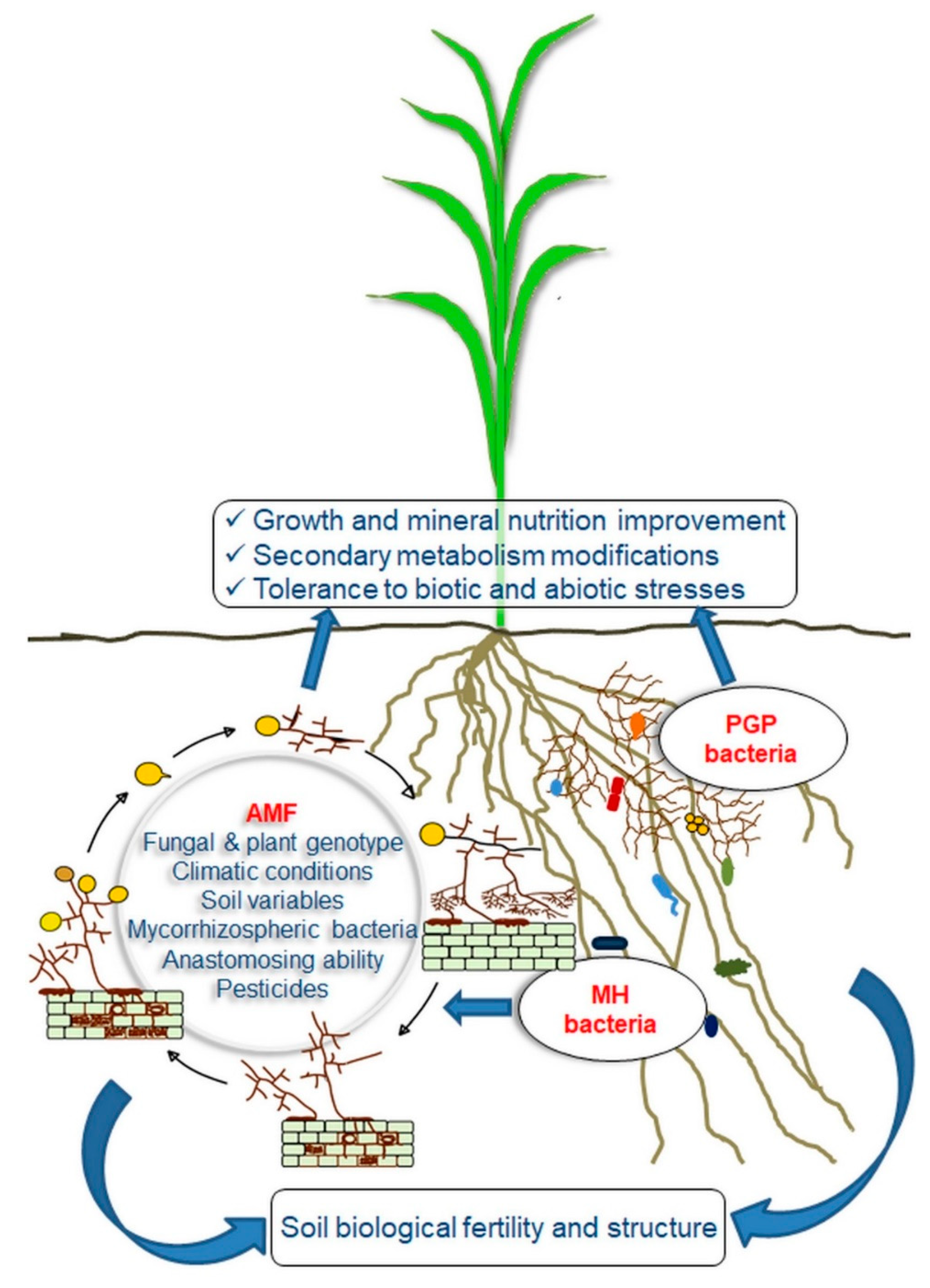
Agronomy Free Full Text Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi And Associated Microbiota As Plant Biostimulants Research Strategies For The Selection Of The Best Performing Inocula Html

Mushroom Life Cycle Kidspressmagazine Com Stuffed Mushrooms Science For Kids Life Cycles

3 Life Cycle Of A Heteroecious Macrocyclic Rust Fungus Melampsora Download Scientific Diagram
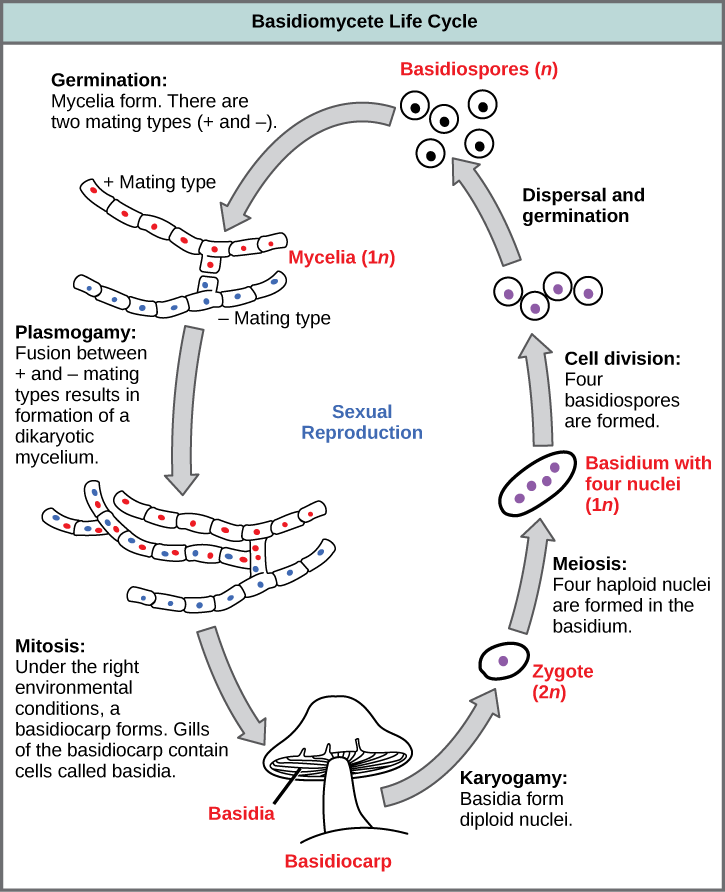
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii
Fungi General Characteristics Classification Morphology Pathogenecity

What Came First The Mushroom Or The Spores Stuffed Mushrooms Life Cycles Plant Science
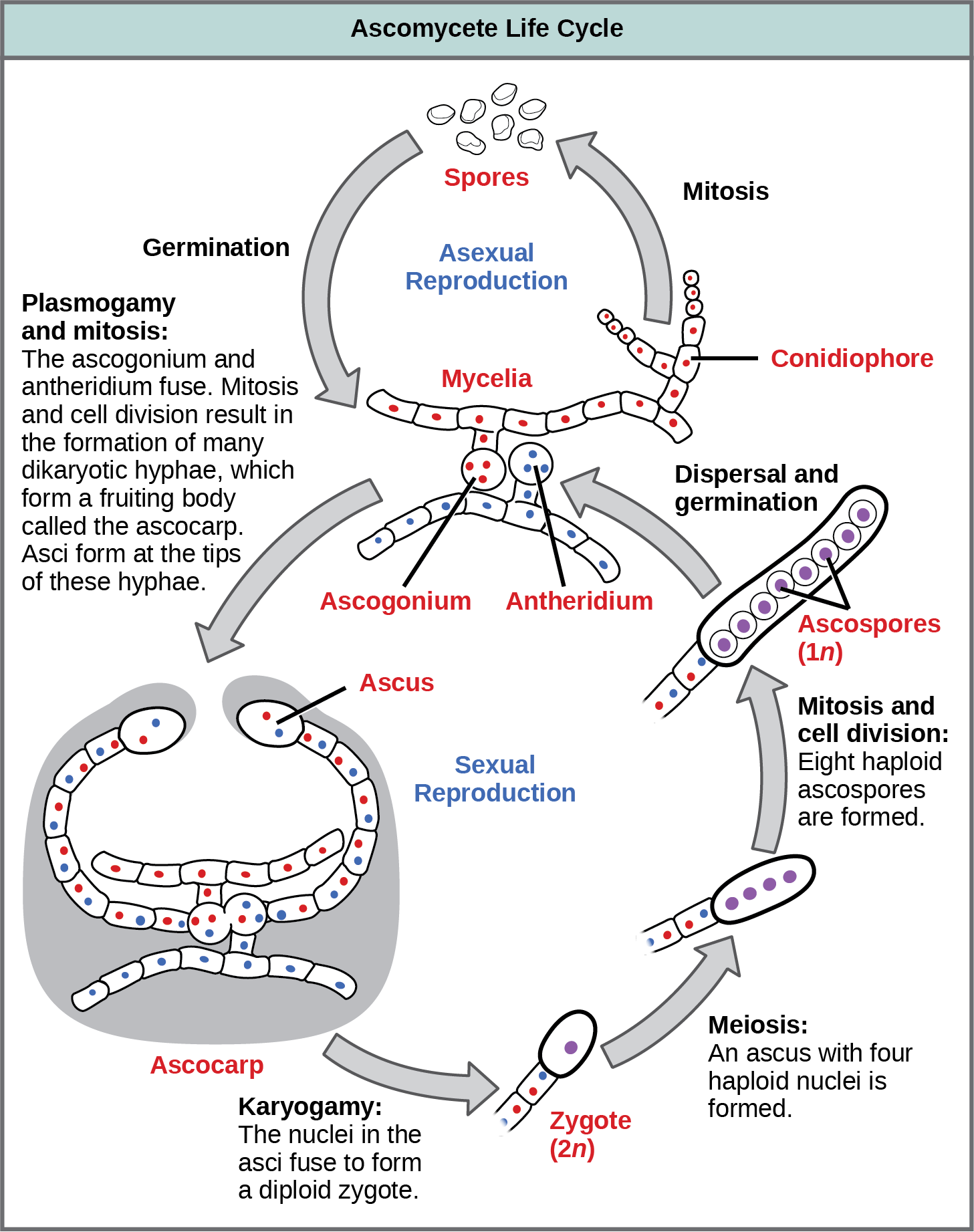
Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e